Disadvantages Of 3D Printing
Don’t get me wrong, forgetting what was inferred by the provocative article title, I truly believe that in the likely decade long run-up from now until the dawn of flawless AI (which is more imminent than you might imagine), the greatest technological event in our history since the arrival of the internet will undoubtedly be the advent of 3D printers becoming as widely commercially viable as Inkjet or Laser Printers. Nevertheless it’s not going to be without its drawbacks; drawbacks it’d serve us well to be conscientious of as the industry begins to burgeon.

Size
Parts printable by a 3D printer are limited by the size of the printer itself. The chamber sizes of commercially available (and affordable) 3D printers, which are commonly small in size enough to be transportable and fit right on your desktop, are proportionately small. The larger models, capable of printing larger shapes and parts, are ordinarily very expensive. Also large parts can take a long time to print on current technology.
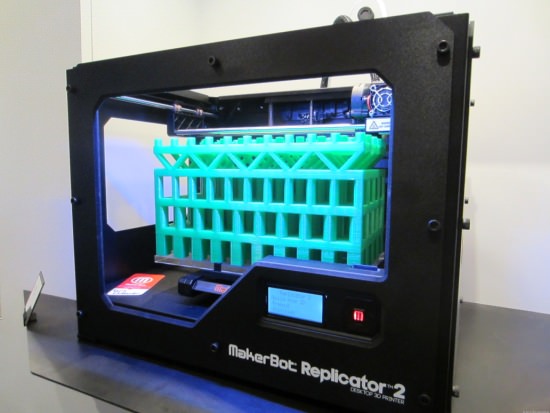

Accuracy
As it stands, parts printed with 3D printing technology are prototypes and test parts most of the time. In order engineers to be able to validate whether or not the prototype or test part is be viable, the dimensions have to be to within a degree of accuracy not yet achievable on the most cutting edge technology. Despite recent advances, most of the materials used in 3D printing still necessitate a disclaimer for the levels of accuracy- there is a margin of around .1 of a millimetre in many cases, which constitutes a catastrophic mistake in many fields of engineering.

Materials
With 3D printing being an additive method (layer after layer), the materials available suited for it are limited- ceramics, resin, plastics. Plastic works for the most part, but can’t have its strength tested in many cases because of the varying melting temperatures. Metal is sometimes usable but dense metal is out of the question, meaning fragility is an issue. Glass and gold are utilised by some specialist companies but are sure not to become commercially available.
Other Disadvantages Include:
- Jobs in manufacturing will be rendered obsolete, in direct correlation to advancements in 3D printing (although design will become a flourishing field); having a negative impact on third world economies.
- There isn’t much happening in the way of recycling initiatives for 3D printing.
- It will be hard or impossible to deter or control people from 3D printing potentially dangerous items including 3D knives, 3D guns, even 3D explosives are doubtlessly imminent.
- Copyright infringements will be rife when the counterfeit printing of copyrighted or patented products and designs becomes widespread and difficult to identify or prevent.
3D printing has of course countless benefits for every field of science, medicine, entertainment, and art- but we mustn’t be tempted in by the novelty of it and lulled into a false sense of security. It is only with careful scrutiny and attention to the aforementioned possible disadvantages that we can come up with ways to move forward safely and with economic conscience.